Axial Fuel Staged Combustion Technology
Release time:
2022-02-21
With the further increase of the outlet temperature of the combustion chamber, the regular lean premixed combustion technology cannot meet the standard requirements for further reduction of NOx.
With the further increase of the outlet temperature of the combustion chamber, the regular lean premixed combustion technology cannot meet the standard requirements for further reduction of NOx. The fuel axial classification is based on the regular lean premixed combustion technology, and the fuel is axially classified. The combustion technology was first proposed by NASA in the clean combustion project in the 1970 s. The staged combustion chamber can reduce NOx emissions for the first time, and then Pratt & Whitney and GE have successfully applied it in aero-engine and gas turbine combustion chambers, with NOx reduced to 35ppm at the lowest. The real large-scale application was around 2010, when GE and Ansaldo achieved large-scale production in G/H and gas turbines.[1].
According to the study of NOx generation mechanism, it is known that the NOx generation rate is proportional to the residence time of the gas in the combustion chamber, and the fuel classification is the technical development for this principle, that is, to reduce the residence time of the secondary fuel in the combustion chamber [2]. As shown in fig. 1, the fuel is axially divided into two stages and enters the combustion chamber for combustion. the first stage combustion can reduce the temperature, the second stage combustion can reduce the residence time of the gas, and the two stages can be independently controlled, and the Lean-Lean strategy, Lean-Rich strategy or Rich-Lean strategy can be adopted. The head stage combustion generally still uses a lean premixed combustion strategy to minimize NOx production.
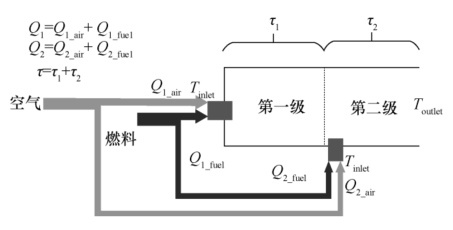
Fig. 1 Axial fuel grading principle[2]
Fig. 1 Principle of axial fuel classification
The fuel staged combustion chamber can not only further improve the temperature of the combustion chamber and control NOx emissions, but also broaden the adjustment ratio range of the thermal load of the combustion chamber, and can perform refined combustion control and strategy optimization for application scenarios with more operating conditions. Purdue University in the United States and the University of Munich in Germany have conducted in-depth research on this technology, and the relevant research conclusions are used in the development of related products of our company.
Combined with the fuel classification design concept of GT36 H class gas turbine combustor of Ansaldo company, the application and design idea of this technology in the field of gas turbine are introduced, as shown in fig. 2.
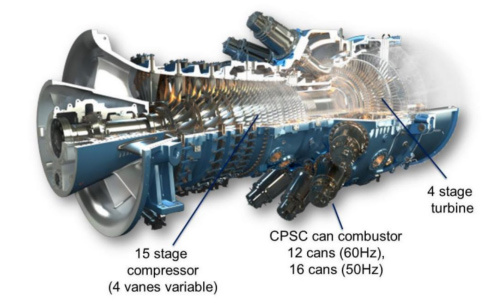
Fig. 2 GT36 Class H Gas Turbine[3]
Fig. 2 GT36 H-class gas turbine
The combustion technology is applied in the combustion chamber of the gas turbine, as shown in Figure 2, the combustion chamber structure form is determined according to the overall structure of the gas turbine, on the basis of which the axial fuel staging combustion chamber is designed, and the details are shown in Figure 3. From this structural diagram, it can be clearly understood that the combustion situation in the stage combustion zone of the axial fuel staging method. Related studies have shown that the key to reducing NOx emissions by axial fuel staged combustion is to adjust the fuel distribution, air distribution and residence time distribution between the first and second stages [2].
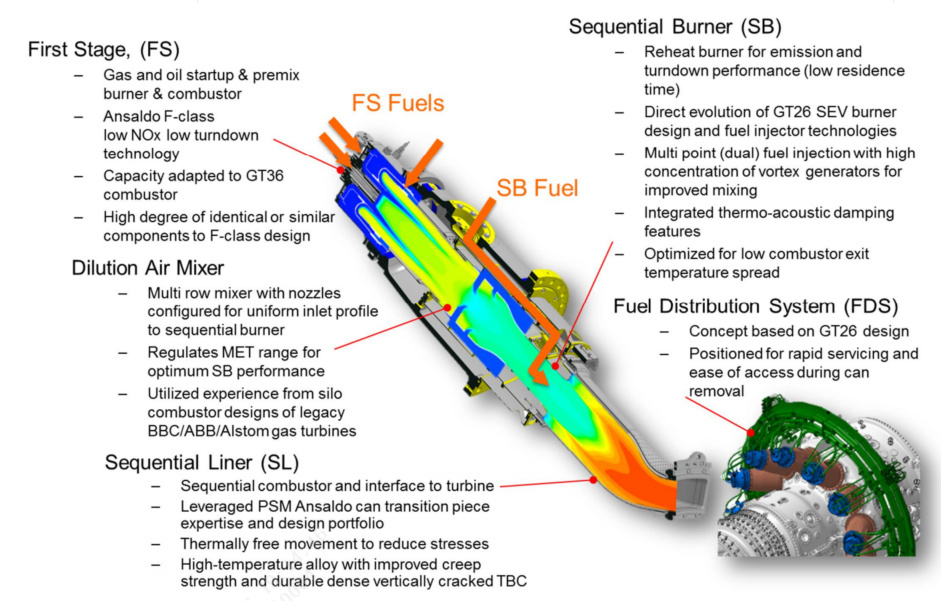
Fig. 3 Detail of GT36 Combustion Chamber[3]
Fig. 3 GT36 CPSC Fire Detection Components
References:
[1] ZHENG Xiang-long. Study on pollutant emission and cross jet flame characteristics of axial staged combustion of fuel [D]. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Institute of Engineering Thermophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences),2020.DOI:10.27540/d.cn ki.ggrws. 2020.000048.
[2] Li Suhui, Zhang Huihua, Wu Yuxin. Review of advanced combustion technology for future gas turbine [J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Natural Science Edition),2021,61(12):1423-1437.DOI:10.16511/j.cn ki.qhdxxb. 2022.25.001.
[3] PENNELL D A,BOTHIEN M R,CIANI A,etal.An introduction to the Ansaldo GT36 constant pressure sequentialcombustor [C]// ASME Turbo Expo 2017: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition. Charlotte,NorthCarolina,USA:ASME,2017.
Contact Us
11/F, Building 1, Guozheng Center, 497 Zhengli Road, Yangpu District, Shanghai

Follow us